|
Back Unit 5.3
|
Home Cover Page
|
Top Annexes
|
Next Referance
|
Annexes
| Name of teacher: | Name of school: |
Subject: Chemistry |
Grade and section: Grade 9 |
Date of lesson: |
Unit of lesson: The Structure of the Atom |
Sub-unit of lesson: Discovery of the sub-atomic particles |
Topic of lesson: Discovery of the Electron |
Competencies: After the lesson Students will be able to
Rationale of the topic: most of the properties of the elements like reactivity and bonding depend on the electrons in their atoms. The number of electrons and their arrangements in the atom are also the basis for the classification of the elements in the periodic table. Understanding the experimental procedures of the discovery of electron helps the students to know how scientific methods are used to explore in to the atoms. |
|
Stage |
Contents |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Assessment activities |
Starter activities(5minutes) |
Review of the modern atomic theory |
|
|
|
Main activities(28 minutes) |
The cathode ray tube Properties of cathode rays
|
to explain the following observations giving reasons
|
Each group registers the findings of their discussion and present to the class.
|
Asking why:
|
Concluding activities (7minutes) |
|
|
|
Ask the students how from the experiment Thomson came to state
|
Figures
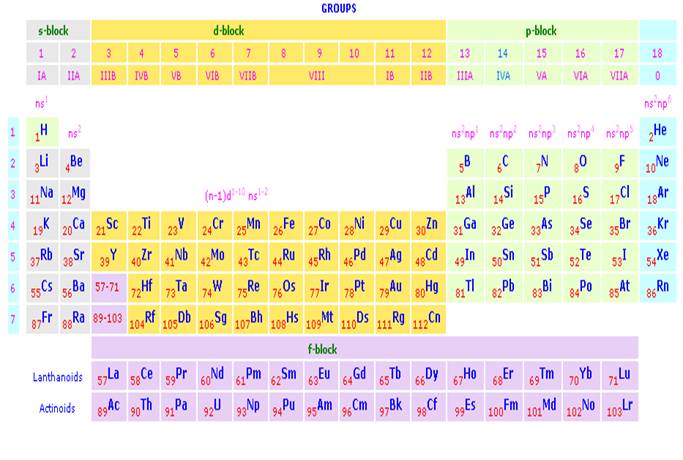
The Periodic Table of the Elements

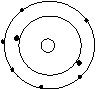
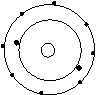
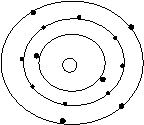
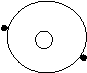
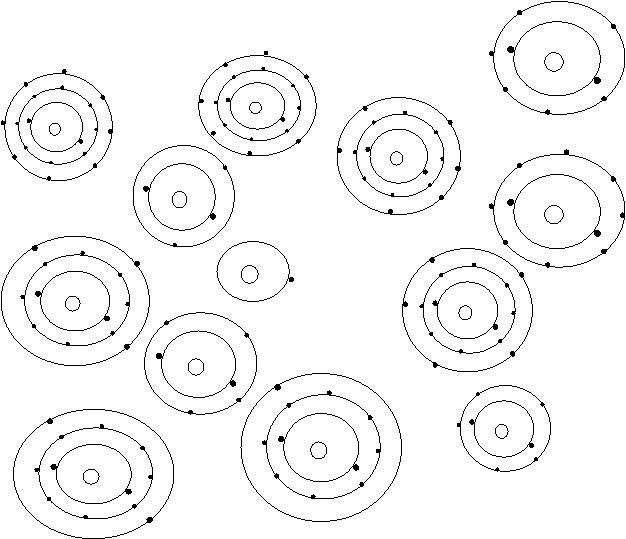
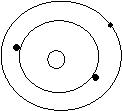
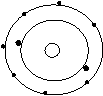
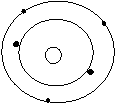
Bohr’s Atomic Models of the First 18 Elements
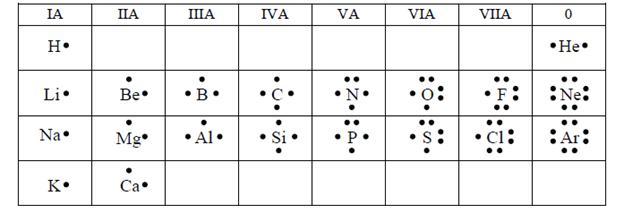
Lewis formula of the first 20 elements