
Fig.11.1 Alcoholic fermentation of yeast
|
Back Lesson 10
|
Home Cover Page
|
Top Lesson 11
|
Next Lesson 12
|
Lesson Eleven: Anaerobic Respiration
Materials
Anaerobic respiration does not consume oxygen. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. It takes place in the cytoplasm of cells. If no oxygen is available to the cell, the pyruvate resulted from glycolsis undergoes fermentation.
Suggested teaching Methodology: - Lecture, Group work and experiment.
Fermentation is the process by which cells release energy without oxygen. Recall that in cellular respiration the cell first breaks glucose into smaller molecules. This releases a small amount of energy only about 2 ATP molecules. Without oxygen, aerobic respiration cannot take place. In eukaryotic cells, instead of entering the mitochondria, these smaller molecules stay in the cytoplasm, where fermentation occurs.
Essential questions/posing problem
There are two main types of fermentation: alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation. Both types of fermentation break sugars down to small molecules. In the absence of oxygen, different reactions occur that produce either alcohol and carbon dioxide or lactic acid. In both cases, a small amount of energy is released.
Yeasts and a few other microorganisms like bacteria carry out alcoholic fermentation.
The students are supposed to write the equation of alcoholic fermentation. The equation of alcoholic fermentation is as follows;
C6 H12O6 → CO2 + C2H5OH (Alcohol) + 2 ATP
In alcoholic fermentation, small amount of energy (only 2ATP ) is released. Carbon dioxide and alcohol are produced as by products.
2 ATP +

Fig.11.1 Alcoholic fermentation of yeast

Fig. 11.2: Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals
How do your muscles continue to get energy during high levels of activity when there is not enough oxygen? Muscles can get energy from glucose through fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation: is a type of anaerobic fermentation that takes place in muscles of humans during rapid exercises. In the case of lactic acid fermentation, one molecule of glucose yields only 2 ATP molecules. Lactic acid is produced as by product.
Equation of Lactic acid fermentation:
C6 H12O6 è C3H6O3 (Lactic Acid) + 2 ATP
Lactic acid fermentation process is carried out by some bacteria like the Lactobacillus acidophilus in yogurt.
2ATP +
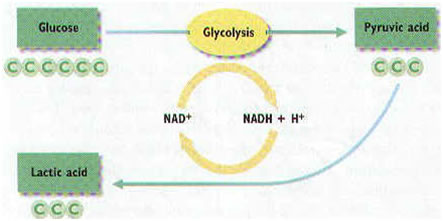
Fig. 11.3: Lactic Acid Fermentation
How can you tell if fermentation releases products?
Procedure
Questions
Tips: Microbes especially yeasts have been used from time immemorial for the production of beverages like wine, beer, whisky, brandy or rum. For this purpose the same yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae used for bread-making and commonly called brewer’s yeast, is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices, to produce ethanol. Do you recollect the metabolic reactions, which result in the production of ethanol by yeast? Depending on the type of the raw material used for fermentation and the type of processing (with or without distillation) different types of alcoholic drinks are obtained. Wine and beer are produced without distillation whereas whisky, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
|---|---|
| Occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria | Occurs in cytoplasm |
| Requires oxygen | Does not require oxygen |
| More efficient | Less efficient |
| Produces about 36-38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule | Produces about 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule |
| Results in the production of H2O and CO2 | Results in the production of alcohol, and CO2 in alcoholic fermentation. Results in the production of lactic acid in lactate fermentation especially in muscle cells of humans. |
| Complete oxidation of glucose | Partial oxidation of glucose |
Table 11.4: Comparison of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
For a real-life application of anaerobic respiration, lead a class discussion on muscle soreness as related to school sports and exercise. Have student’s research lactic acid build-up in muscles, the causes, and any possible treatments.
The students should be paired in groups of 4-5 to discuss the significances of fermentation in daily life.